8 Reasons It’s Harder Than Ever to Rank on Google and Get Organic Traffic

Ranking on Google is harder than ever, but this doesn’t mean you should throw in the towel. Companies still need to be cognizant of SEO. Why? Because the majority of all website traffic – 51 percent of it – comes from organic search, according to data from BrightEdge. All this traffic makes a difference in sales, too: more than 40 percent of revenue is captured by organic traffic.
According to Internet Live Stats, more than 3.5 billion Google searches occur every day. That’s a big pie, but getting a piece of it is becoming more and more difficult. Here are eight reasons why.
1. The Rise of Voice Search
When text messages started replacing phone calls, it seemed like voice communication had gone out of style, but that’s changing again. Google has stated that mobile searches now account for more than 50 percent of total searches. An increasing number of these searches are performed using voice. Smart devices, like Amazon’s Alexa and Google Home, are also contributing to the rise of voice searches.
It might seem like it shouldn’t matter whether people are talking or typing. Either way, they’re searching for the same things, so the search results and ranks should be the same – right? Wrong.
You just have to think about the way people talk versus the way they write to understand why. Writing tends to be much more precise. Speech, on the other hand, is usually much more casual. More often than not, it’s also not as well thought out. To see examples of how this vagueness can result impact search results, check out this article by Mordy Oberstein.
It can be harder to predict – and thus write for – voice searches, but that’s not the only issue. When people use voice search on their mobile devices, they’re not engaging in lengthy research projects. They want simple answers, and they want them fast. They’re not going to scroll through page after page of results on their tiny screens. This means that if your site isn’t one of the first few results, it probably won’t get seen at all.
Voice searches aren’t just making it harder to rank; they’re also making it more important to rank highly.
2. The Increasing Specificity of Searches
As the number of searches increases, so does the specificity. People know exactly what they want, and they count on the search engine to supply it.
Think about it. If someone wants to buy new shoes, they probably have a specific shoe type in mind. They don’t just want shoes – they want red four-inch pumps under $50, for example, or black waterproof boots. They’re increasingly likely to search for these more specific terms, and marketers should take note. The upside of this is that longer, more specific phrases have less competition, making it easier to rank.
Intent goes hand in hand with specificity. If someone searches for “clean boots,” for example, they’re probably looking for instructions on cleaning boots, not shopping for clean boots.
“Determining your customer’s intention borders on mind reading, which is why ConsumerAffairs invests so much in search optimization techniques in relation to artificial intelligence, deep learning and machine learning,” said Zac Carman, CEO of ConsumerAffairs, speaking to Newsmax.
Google uses an algorithm called RankBrain to determine the user intent behind searches. This is the third most important factor in ranking.
3. The Importance of Inbound Links
Inbound links from high-quality sites are the holy grail of SEO. They’re extremely useful – in fact they’re one of the most important ranking factors.
Inbound links are also difficult to control. After all, that high-quality site has to choose to link to your site. You can’t choose it for them. You have to entice them with quality and authoritative content that they’ll want to link to.
As a result, it’s not surprising that 41 percent of larger companies believe that link building is the most difficult part of SEO, according to research from Ascend2 and Conductor.
4. Competition from the Big Leagues
The internet seems like the one place where the little guy should have an easy time competing in the big leagues. Unfortunately, this isn’t exactly true.
The bigger a company is, the more likely it is to get inbound links, online mentions and direct traffic. All of this means that site is perceived to have more authority. The result is a better rank. Fame begets fame – making it more difficult for smaller businesses to get any attention.
Smaller companies have to work much harder to get good rankings.
Also, because well-known companies take up prime real estate on the search results page, smaller, local companies have fewer chances. If you search for a common type of business, you’ll likely see several local results mixed in with sites for large, national companies. If you’re competing for those local spots, the spots taken up by national giants reduce your chances.
5. The Increased Length of Content
Content has gotten longer.
According to research from Backlinko, the average word count for first page results on Google is 1,890. Looking at the first 10 search results, the top four have significantly higher words counts than the bottom four.
In other words, length matters.
According to John Lincoln, a digital marketing teacher at the University of California San Diego, people associate length with expertise, and longer content is more likely to result in shares and engagement. To read more about why longer content works, check out his article, the SEO and User Science Behind Long-Form Content.
But even without understanding the science behind it, the consequence is clear. If you want your website to rank well, you need to produce long, in-depth content.
6. Fewer Results Per Page
When you conduct a Google search, you typically get multiple pages of results – but how often do you go past the first page? If you’re like most people, it’s not often.
Most people only look at the first page. This means that even if you don’t rank first, as long as you rank on the first page, you’re in good shape.
Which raises an important question: how many results appear on the first page?
The answer is, not as many as there used to be.
According to research from Searchmetrics, the average number of organic mobile search results has decreased from 10 to 8.5. That’s one to two fewer chances to get on the first page. And if you don’t get on that first page, you probably won’t get many views at all.
7. The Growth of the Internet
How many websites do you think there are?
According to Internet Live Stats, there are more than 1.3 billion websites online right now. Even allowing for the fact that some of these sites – around 75 percent – are inactive, that’s still an overwhelmingly large number.
For comparison, in June 2008, there were only 172,338,726 websites. That’s a huge number to be sure, but it’s only a fraction of what currently exists. In June 1998, only 2,410,067 websites existed. Two years earlier, that figure was 257,601.
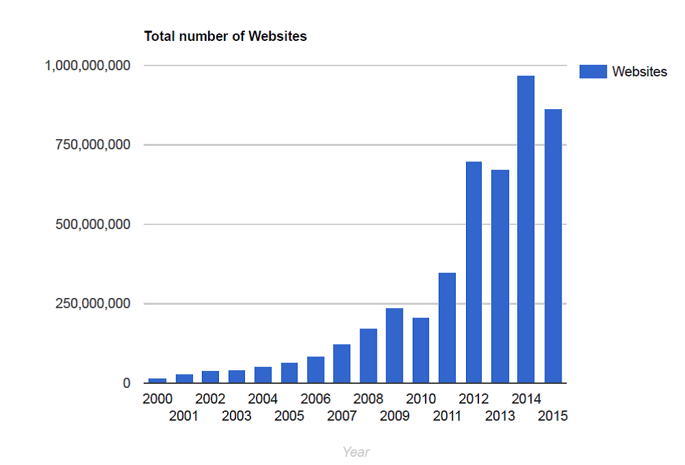
The growth of the internet also represents a growth in competition. There are simply too many sites for any person to visit in a lifetime. In 2015, the average number of users per website was a measly 3.7. In 1995, each site had an average of 1,908 users. That’s an enormous drop.
8. The Creation of Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are results that sometimes show up on Google searches. They appear before the ranked sites, and they provide a quick answer pulled from the internet. They’re very convenient for users, who don’t have to click through the results to get an answer to their question.
They may be less desirable for businesses trying to earn traffic.
After all, the whole point of featured snippets is that users don’t have to go another website. The answers are right there in the search results. HubSpot ran the numbers to see how this feature has impacted blog traffic, and the results weren’t pretty.
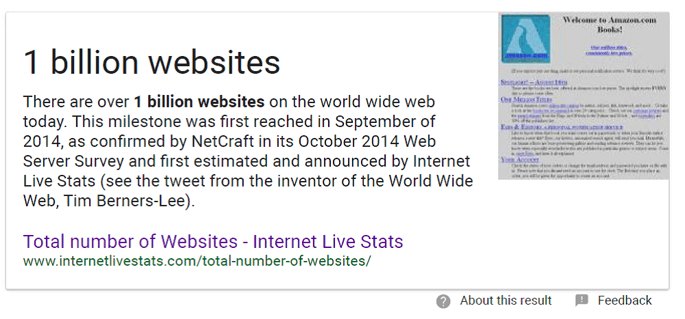
The above example is a featured snippet that shows at the top of the page when I search, “How many websites are there?” Because the information is displayed right there, I may not click through to the website, thereby hurting the ranking company’s organic traffic results. I can use their content without clicking.
Another change from Google involves meta tags. The meta description limit has just been increased to 320 characters. It’s important to use these characters wisely, both to compete with featured snippets and to entice users to click.
So How Can You Rank on Google and Get Organic Traffic?
The takeaway is not that organic ranking is impossible. The takeaway is that it’s difficult but essential. Instead of giving up or plugging away with old tactics that no longer work, companies need to adjust their strategies for the realities of the modern world.
Here are seven steps you can take now:
- Focus on adding new original quality content to your site every week. According to a report from Econsultancy, 45 percent of companies believe that content marketing is highly integrated with SEO strategy.
- Write content for voice search. This means anticipating common questions and providing direct answers. Search Engine Journal has more tips on how to accomplish this.
- Think longer. Remember, though, that quality also matters. Make sure you’re increasing your word count with useful, insightful information, not fluff.
- Supplement with pay-per-click advertising. Organic results are great, but sometimes to compete in the modern world, you need to go paid.
- Drive your authority with social and offline channels. This is a great way to trigger direct visits so you’re not entirely dependent on search rankings.
- Don’t neglect the basics. Your page titles, meta tags, header tags, photos and videos still matter. SEO has evolved, but much of the foundation remains the same.
- Extend meta tags to 320 characters, and make sure those characters entice users to click.
Need great content to drive your SEO strategy? We can help. Contact us to learn more, Or, find out why content writing is no longer optional– it’s a basic business survival skill.
